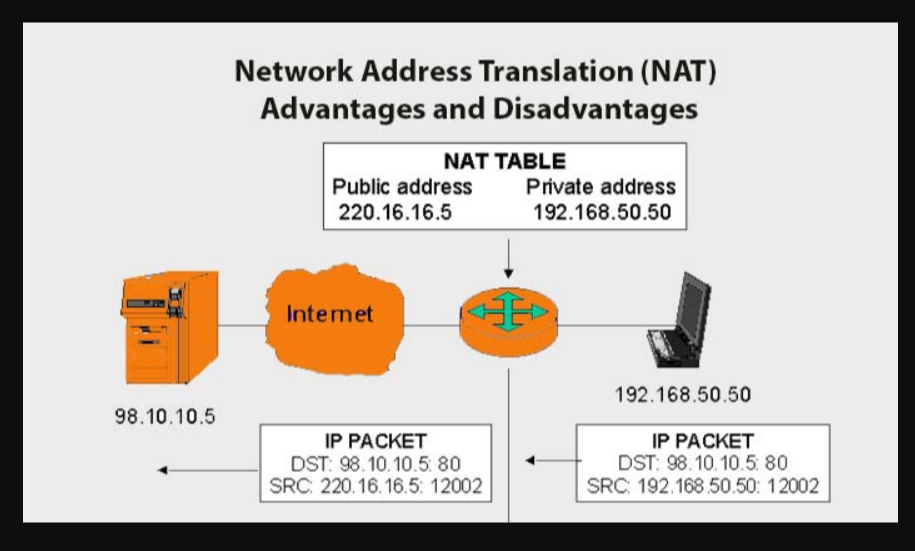
Before discussing the configuration from the NAT in the following paragraphs we’ll discuss the NAT pros and cons.
NAT Advantages
- The primary benefit of NAT is it can avoid the depletion of IPv4 addresses. It conserves the general public IPv4 address by permitting the privatization of intranets. NAT save the addresses using application port-level multiplexing. With Port Address Translation, the hosts with private IPv4 addresses can share just one public IPv4 address for those exterior communications.
- Network Address Translation (NAT) offers elevated versatility when connecting towards the public Internet. We are able to implement a backup pool, and cargo-balancing pools to make sure reliable public network connections.
- If a network utilizes a public Ip, first the administrator can get a previous address space like a network grows, the risk of getting IP addresses in the same Ip class is minimal as well as zero. However in situation of utilizing private address and NAT for exterior traffic with a couple addresses, a company doesn’t have to buy IP addresses for each computer being used there’s a substantial cost saving because of using the entire process of Network Address Translation.
- Network Address Translation (NAT) enables to apply your own private IPv4 addressing plan and stop the interior address alterations in situation of altering the company.
- Network Address Translation (NAT) provides additional security by masking the initial source and destination addresses. The non-public systems don’t advertise their addresses or internal topology, therefore, feel at ease when used along with NAT to achieve controlled exterior access.
Disadvantages of NAT
With NAT advantages the NAT several disadvantages. Due to the host on the web communicates directly using the NAT-enabled router instead of the particular host within the private network. That situation creates several issues.
- Network Address Translation (NAT) consumes the processor and memory because NAT have to translate IPv4 addresses for those outgoing and incoming IPv4 datagram and also to keep your translation details in memory.
- It slows lower the network performance, so that it results in a condition in real-time protocols. Zinc heightens switching delays since the translation of every IPv4 address inside the packet headers needs time to work.
- When using, NAT the finish-to-finish addressing sheds. Several Internet protocols and applications basis on finish-to-finish addressing in the source towards the destination therefore many applications fail to work with NAT. Some applications use physical addresses, instead of the qualified website name, cannot achieve the destinations when utilizing a NAT router.
- In the situation of utilizing NAT, the finish-to-finish IPv4 traceability isn’t feasible. The tracing from the packets is a lot difficult due to altering the address over multiple NAT hops. This will make troubleshooting difficult.
- NAT also make difficult using tunnelling